Oops
Object-oriented blueprint started right from the moment computers were invented. Programming was there, and programming approaches came into the picture. Programming is basically giving sure instructions to the calculator.
At the kickoff of the computing era, programming was ordinarily limited to car language programming. Machine language ways those sets of instructions that are specific to a particular auto or processor, which are in the form of 0's and one'south. These are sequences of $.25 (0100110…). But it's quite difficult to write a plan or develop software in machine language.
Information technology's really impossible to develop software used in today's scenarios with sequences of bits. This was the main reason programmers moved on to the next generation of programming languages, developing assembly languages, which were near enough to the English language to easily understand. These assembly languages were used in microprocessors. With the invention of the microprocessor, assembly languages flourished and ruled over the manufacture, merely it was not enough. Again, programmers came up with something new, i.e., structured and procedural programming.
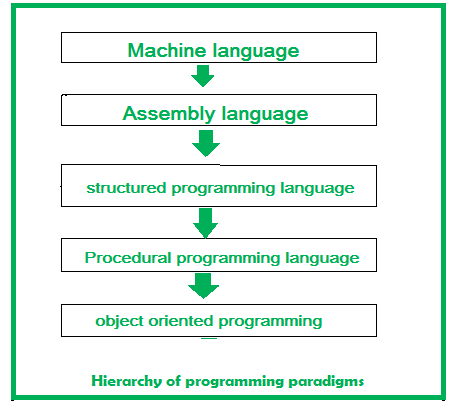
Structured Programming –
The basic principle of the structured programming arroyo is to divide a program into functions and modules. The use of modules and functions makes the program more than understandable and readable. It helps to write cleaner code and to maintain control over the functions and modules. This arroyo gives importance to functions rather than data. It focuses on the development of large software applications, for example, C was used for modern operating system development. The programming languages: PASCAL (introduced by Niklaus Wirth) and C (introduced by Dennis Ritchie) follow this approach.
Procedural Programming Approach –
This approach is also known every bit the top-downwards approach. In this arroyo, a programme is divided into functions that perform specific tasks. This approach is mainly used for medium-sized applications. Information is global, and all the functions can access global data. The bones drawback of the procedural programming approach is that data is not secured because data is global and can be accessed past any part. Programme command menstruation is achieved through function calls and goto statements. The programming languages: FORTRAN (adult by IBM) and COBOL (developed by Dr. Grace Murray Hopper) follow this approach.
These programming constructs were adult in the late 1970s and 1980s. There were still some bug with these languages, though they fulfilled the criteria of well-structured programs, software, etc. They were not as structured as the requirements were at that time. They seem to be over-generalized and don't correlate with real-time applications.
To solve such kinds of problems, OOP, an object-oriented approach was developed as a solution.
The Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Approach –
The OOP concept was basically designed to overcome the drawback of the above programming methodologies, which were not so close to real-world applications. The need was increased, merely still, conventional methods were used. This new approach brought a revolution in the programming methodology field.
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is goose egg simply that which allows the writing of programs with the help of certain classes and existent-fourth dimension objects. Nosotros tin say that this approach is very shut to the real-world and its applications because the country and behaviour of these classes and objects are about the same as real-world objects.
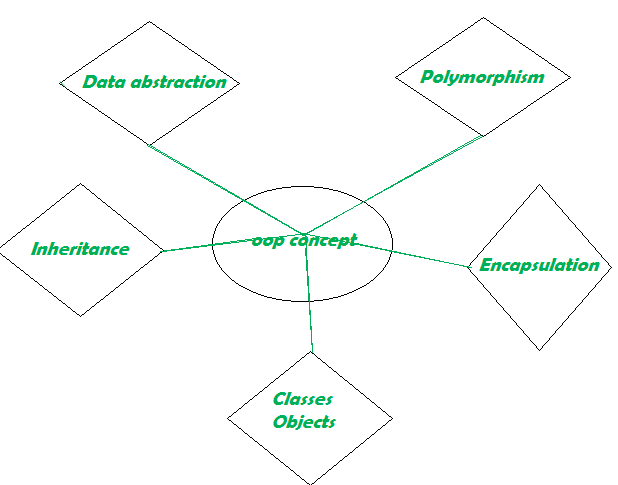
Let's go deeper into the general concepts of OOP, which are given below:
What Are Class & Object?
It is the basic concept of OOP; an extended concept of the construction used in C. It is an abstract and user-defined information type. It consists of several variables and functions. The primary purpose of the class is to store data and information. The members of a form define the behaviour of the class. A class is the design of the object, but also, nosotros can say the implementation of the class is the object. The grade is not visible to the world, just the object is.
CPP
Course car
{
int car_id;
char colour[4];
bladder engine_no;
double distance;
void distance_travelled();
float petrol_used();
char music_player();
void display();
}
Hither, the class car has properties car_id, colour, engine_no, and distance. It resembles the existent-world car that has the same specifications, which tin can be declared public (visible to everyone exterior the class), protected, and individual (visible to none). Also, there are some methods such as distance_travelled(), petrol_used(), music_player() and display(). In the code given below, the auto is a class and c1 is an object of the machine.
CPP
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class car {
public :
int car_id;
double distance;
void distance_travelled();
void display( int a, int b)
{
cout << "car id is=\t" << a << "\ndistance travelled =\t" << b + 5;
}
};
int chief()
{
automobile c1;
c1.car_id = 321;
c1.altitude = 12;
c1.brandish(321, 12);
return 0;
}
Information Abstraction –
Brainchild refers to the act of representing important and special features without including the background details or caption most that feature. Data abstraction simplifies database design.

- Physical Level:
Information technology describes how the records are stored, which are frequently hidden from the user. It can be described with the phrase, "block of storage." - Logical Level:
It describes data stored in the database and the relationships between the data. The programmers generally work at this level as they are aware of the functions needed to maintain the relationships betwixt the data. - View Level:
Awarding programs hibernate details of data types and information for security purposes. This level is generally implemented with the help of GUI, and details that are meant for the user are shown.
Encapsulation –
Encapsulation is 1 of the fundamental concepts in object-oriented programming (OOP). It describes the thought of wrapping data and the methods that work on data within one unit, e.one thousand., a class in Java. This concept is oftentimes used to hide the internal state representation of an object from the outside.
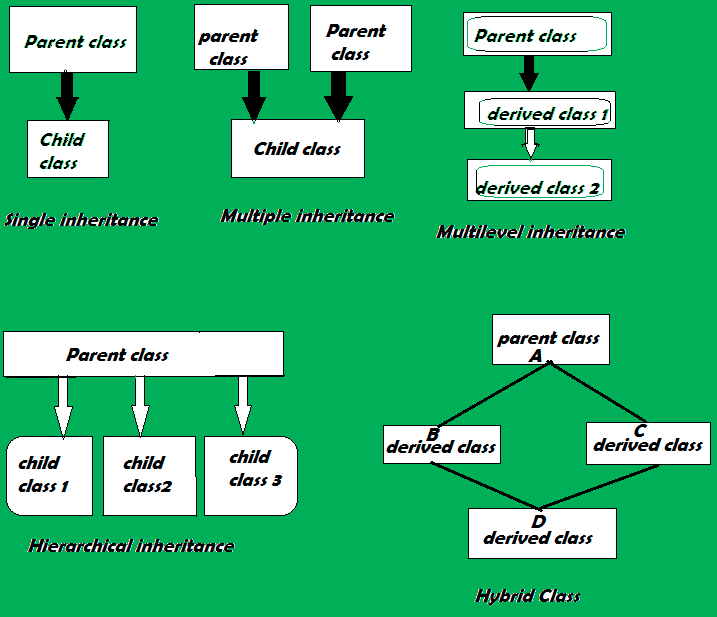
Inheritance –
Inheritance is the ability of 1 form to inherit capabilities or properties of another class, called the parent class. When nosotros write a class, we inherit properties from other classes. So when nosotros create a class, we do not need to write all the properties and functions again and again, equally these can be inherited from another class that possesses information technology. Inheritance allows the user to reuse the code whenever possible and reduce its redundancy.
Java
import coffee.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(Cord[] args)
{
System.out.println( "GfG!" );
Dog canis familiaris = new Dog();
domestic dog.proper name = "Bull dog" ;
dog.color = "Brown" ;
domestic dog.bark();
dog.run();
Cat cat = new True cat();
true cat.name = "Rag doll" ;
cat.blueprint = "White and slight dark-brown" ;
cat.meow();
cat.run();
Animal animal = new Animal();
animal.name = "My favourite pets" ;
animal.run();
}
}
form Creature {
String proper name;
public void run()
{
System.out.println( "Fauna is running!" );
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
String color;
public void bark()
{
System.out.println(name + " Wooh ! Wooh !"
+ "I am of color " + color);
}
}
class True cat extends Animal {
String pattern;
public void meow()
{
Organization.out.println(name + " Meow ! Meow !"
+ "I am of colour " + pattern);
}
}
Polymorphism –
Polymorphism is the ability of data to exist processed in more than than ane course. Information technology allows the performance of the same job in various means. It consists of method overloading and method overriding, i.e., writing the method one time and performing a number of tasks using the aforementioned method proper name.

CPP
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void output( float );
void output( int );
void output( int , bladder );
int main()
{
cout << "\nGfG!\due north" ;
int a = 23;
float b = 2.3;
output(a);
output(b);
output(a, b);
return 0;
}
void output( int var)
{
cout << "Integer number:\t" << var << endl;
}
void output( float var)
{
cout << "Float number:\t" << var << endl;
}
void output( int var1, float var2)
{
cout << "Integer number:\t" << var1;
cout << " and bladder number:" << var2;
}
Some important points to know about OOP:
- OOP treats information equally a critical element.
- Emphasis is on data rather than procedure.
- Decomposition of the problem into simpler modules.
- Doesn't allow data to freely catamenia in the entire system, ie localized control flow.
- Data is protected from external functions.
Advantages of OOPs –
- It models the real earth very well.
- With OOP, programs are easy to sympathise and maintain.
- OOP offers code reusability. Already created classes tin exist reused without having to write them once again.
- OOP facilitates the quick development of programs where parallel development of classes is possible.
- With OOP, programs are easier to test, manage and debug.
Disadvantages of OOP –
- With OOP, classes sometimes tend to be over-generalized.
- The relations among classes become superficial at times.
- The OOP pattern is tricky and requires appropriate knowledge. Also, i needs to do proper planning and design for OOP programming.
- To programme with OOP, the programmer needs proper skills such equally design, programming, and thinking in terms of objects and classes, etc.
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/oops-object-oriented-design/
0 Response to "Oops"
Post a Comment